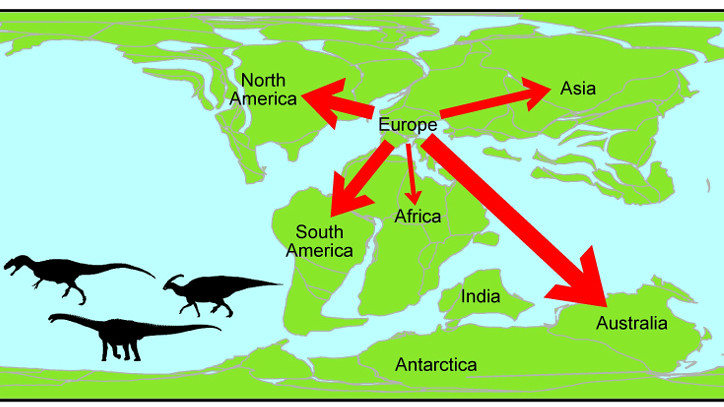
Europe saw an exodus of dinosaurs from the continent in the Early Cretaceous period, scientists using ‘network theory’ to track their movements around the world have shown.
Surprisingly all dinosaur connections found between Europe and other continents during the Early Cretaceous period (125-100 million years ago) were out-going. That is, while dinosaur families were leaving Europe, no new families were migrating into Europe.
Co-author Dr James Sciberras, from the Department of Biology & Biochemistry at the University of Bath, worked with colleagues at the University of Leeds on the network theory analysis.
Dr Sciberras said: “Network theory allows us to track the relationships between related data points, in this example dinosaur fossils, allowing us to show this possible exodus effect.
“Network theory has been studied in physics for a number of years, however it is finally permeating into other disciplines. This idea that most things can, and should, be considered in the context of the whole system will lead to some exciting new findings in a wide range of fields.”
Lead researcher Dr Alex Dunhill from the University of Leeds, said: “This is a curious result that has no concrete explanation. It might be a real migratory pattern or it may be an artefact of the incomplete and sporadic nature of the dinosaur fossil record.”
The research, published today in the Journal of Biogeography, also confirms previous studies that found dinosaurs continued to migrate to all parts of the world after the ‘supercontinent’ Pangaea split up.
Dr Dunhill said: “We presume that temporary land bridges formed due to changes in sea levels, temporarily reconnecting the continents.”
“Such massive structures – spanning, for example, from Indo-Madagascar to Australia – may be hard to imagine. But over the timescales that we are talking about, which is in the order of tens of millions of years, it is perfectly feasible that plate tectonic activity gave rise to the right conditions for such land bridges to form.”
The researchers used the Paleobiology Database that contains every documented and accessible dinosaur fossil from around the world. Fossil records for the same dinosaur families from different continents were cross-mapped for different time periods, revealing connections showing how they migrated.
Some regions of the world including Europe have extensive fossil records from a long history of palaeontology digs, while other parts of the world have been largely unexplored. To help account for this disparity in fossil records, which could otherwise skew the findings, the researchers applied a filter to the database records to only count the first time that a dinosaur family connection occurred between two continents.
The findings support the idea that, although continental splitting reduced intercontinental migration of dinosaurs, it did not stop completely.
While network theory is commonly used in computer science for quantifying internet data, such as friend connections on Facebook, it has only recently been applied to biology research and this is the first study to use it to on dinosaur research.
Further information
The research paper, Dinosaur biogeographical structure and Mesozoic continental fragmentation: a network-based approach, is published in the Journal of Biogeography. (DOI:10.1111/jbi.12766)