Molecular interactions between 1-10nm can be detected in cell biology by using Time-resolved Förster Resonance Energy Transfer detected by Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM). Cell Biophysics laboratory (7W 3.11) has two FLIM setups one in the time domain and another in the frequency domain. Expertise and training are provided by the specialised engineer in Cell Biophysics Laboratory. These set-ups are part of the Centre for Therapeutic Innovation (CTI-Bath).
Our Two-Photon Time Domain FLIM has a Ti-Sapphire solid-state laser that can be fully modulated between 810 and 930 nm. This Nikon TE 2000 inverted microscope has a similar resolution to a confocal microscope. The advantage of the two-photon as opposed to confocal is that it will not bleach the biological samples. This set-up is ideal for investigating new molecular pathway interactions in live/ fixed cells and in spheroids or small organoids. It also has microinjection facilities.
Relevant References:
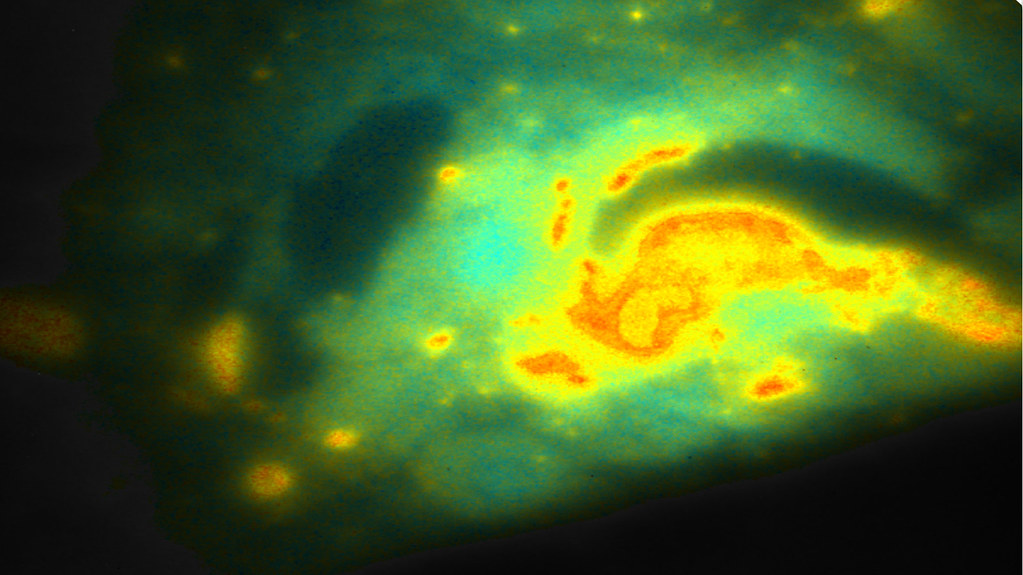
Image caption: determination of interactive states of immune check point regulators, programme death ligand1 and programme death receptor (PDL1-PD1) on fixed lung carcinoma. The red regions have high interactive states (measured molecular distance is 5.5nm) and blue regions the ligand and receptor do not interact. Interactions are determined by High-throughput automated multiple frequency domain Fluorescence imaging microscope using amplified coincidence-Förster resonance energy transfer. (Courtesy of Cell Biophysics Laboratory- Centre for Therapeutic Innovation 2023).